学习自:https://qiankunli.github.io/2021/08/18/gpu.html
NVIDA官方手册:https://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/cuda-c-programming-guide/index.html#abstract
整体感知
- GPU 的整个处理过程是一个流式处理(Stream Processing)的过程,分支条件少(少用控制语句)
- 每个GPU核心(是个电路) 只有 取指令、指令译码、ALU 以及执行这些计算需要的寄存器和缓存
现代 CPU 里的晶体管变得越来越多,越来越复杂,其实已经不是用来实现“计算”这个核心功能,而是拿来实现处理乱序执行、进行分支预测,以及高速缓存部分。GPU把这些部分去除了
the GPU can hide memory access latencies with computation, instead of relying on large data caches and complex flow control to avoid long memory access latencies, both of which are expensive in terms of transistors.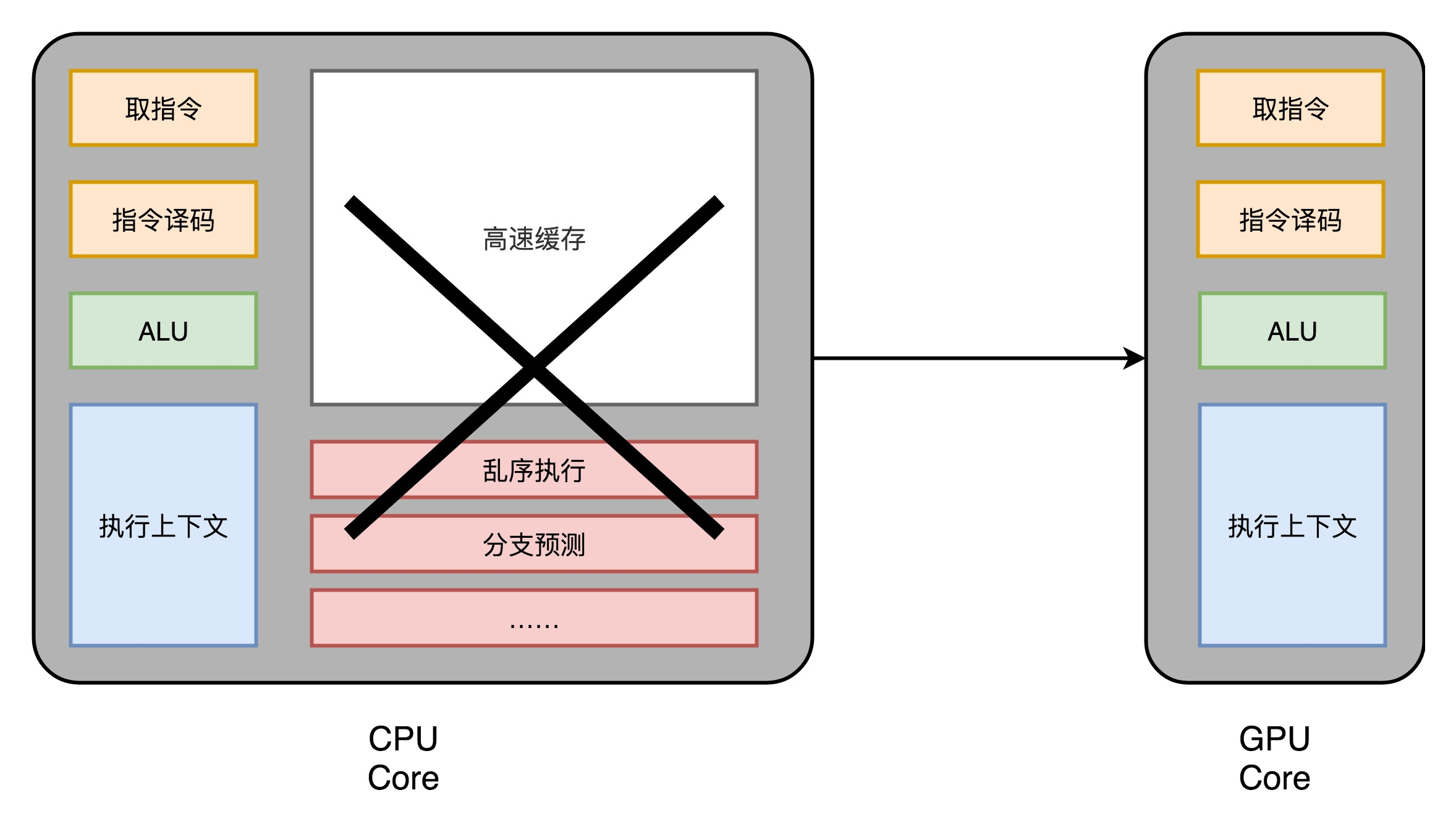
- 一个 GPU :多个这样并行的 GPU 电路
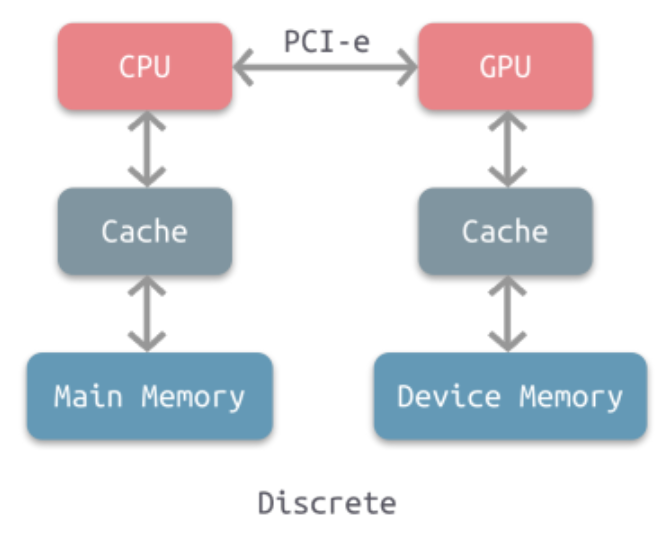
- 内存访问(分离式架构):(gpu作为外设可以访问cpu内存,但)cpu 和gpu 最擅长访问自己的内存
GPU 硬件架构
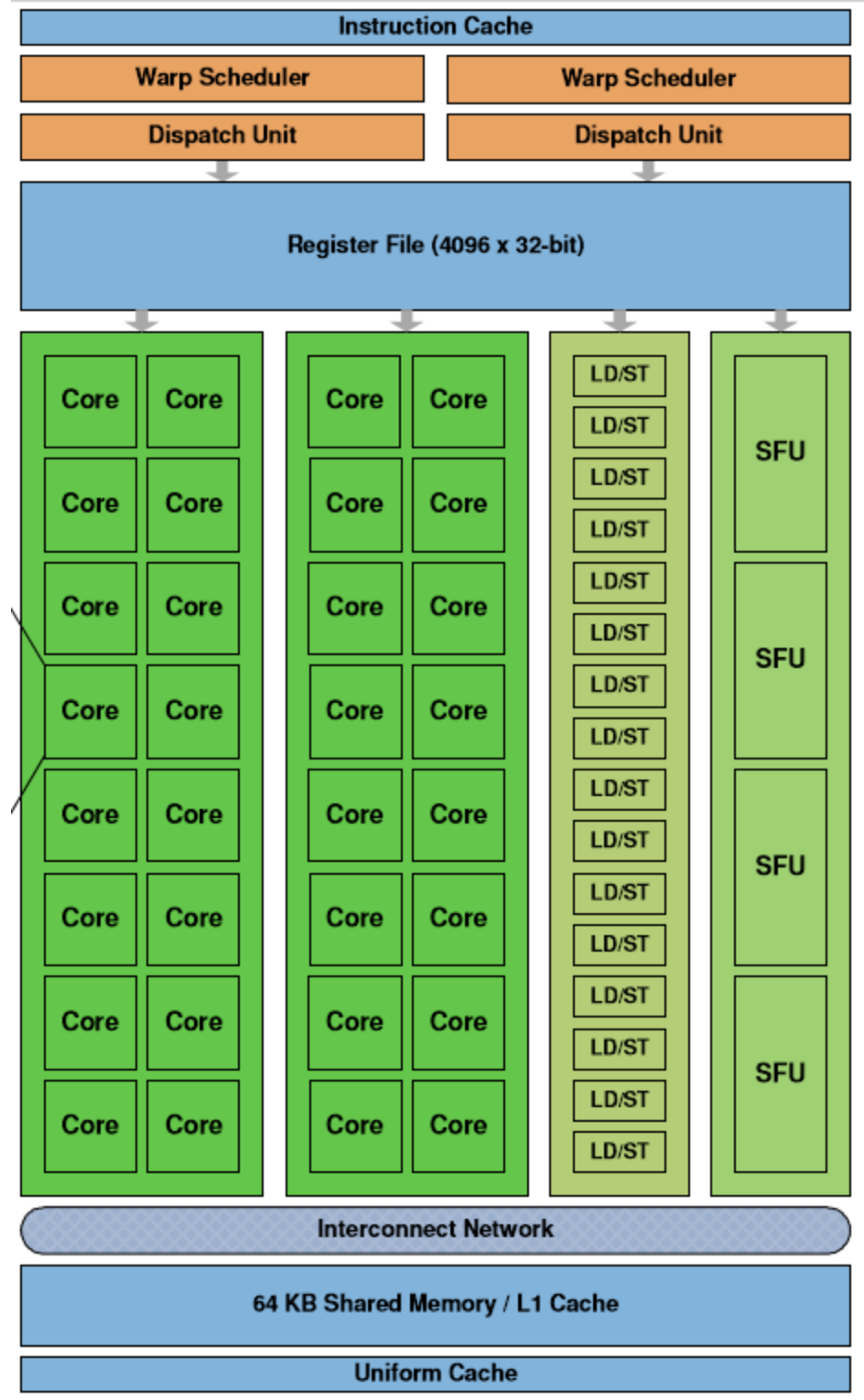
- 每个 GPU 都由一组 SM(流式多处理器Streaming Multiprocessor,核心Core) 构成;
- 线程调度器(Warp Scheduler):线程束(Warp)是最基本的单元,每个线程束中包含 32 个并行的线程,它们使用不同的数据执行相同的命令,调度器会负责这些线程的调度;
- 访问存储单元(Load/Store Queues):在核心和内存之间快速传输数据;
- 特殊函数的计算单元(Special Functions Unit、SPU)
- 存储和缓存数据的寄存器文件(Register File)
- 共享内存(Shared Memory)
执行速度
CUDA 核心在每个时钟周期都可以准确的执行一次整数或者浮点数的运算
CPU 与GPU 协作(分离式)
分离式:
- GPU 是一个外设,有驱动程序
MMIO: Memory-Mapped I/O
锁页:操作系统常用的操作,可以使硬件外设直接访问物理内存。”被锁定“的页面被os标记为不可被os 换出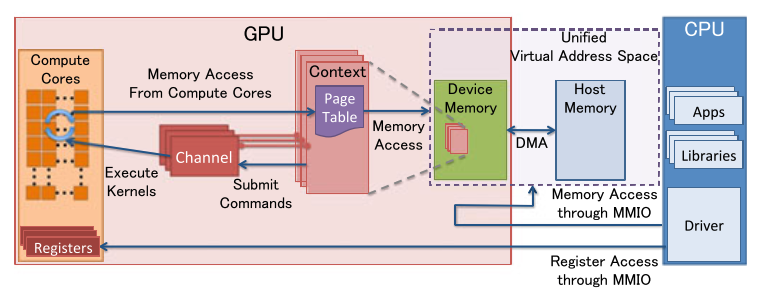
- 驱动程序提供的接口:
- 一般的外设:输出数据地址 command_operation(输入数据地址)
这个意思是类似于函数申明:cpu控制向输入数据地址写数据,调用接口,等中断,然后从输出数据地址读数据
- gpu:输出数据地址 command_operation(指令序列,输入数据地址)
- 典型工作流程:
- 应用层(cpu上执行)调用某个会调用GPU的API,如 OpenGL 或 CUDA
- OpenGL 或 CUDA 库,通过 UMD (User Mode Driver),提交 workload 到 KMD (Kernel Mode Driver)
- Kernel Mode Driver 写 CSR MMIO,把它提交给 GPU 硬件
- GPU 硬件开始工作… 完成后,DMA 到内存,发出中断给 CPU
- CPU 找到中断处理程序 —— Kernel Mode Driver 此前向 OS Kernel 注册过的 —— 调用它
- 中断处理程序找到是哪个 workload 被执行完毕了,…最终驱动唤醒相关的应用
- 典型工作流程:
- 一般的外设:输出数据地址 command_operation(输入数据地址)
CUDA(一种GPU驱动程序)编程
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/34587739
nvida官方手册:https://developer.nvidia.com/zh-cn/blog/cuda-intro-cn/
编程模型
这些抽象提供了细粒度的数据并行和线程并行,嵌套在粗粒度的数据并行和任务并行中。它们指导程序员将问题划分为可以由++线程块++并行独立解决的粗略子问题,并将每个子问题划分为可以由++块内所有线程++并行协作解决的更精细的部分。
- 一个问题(grid)划分为多个线程块(block或者warp;gridDim个),线程块之间独立执行;
- 每个线程块有多个thread(blockDim个),每个线程块对应一个deviceFunction(kernel)
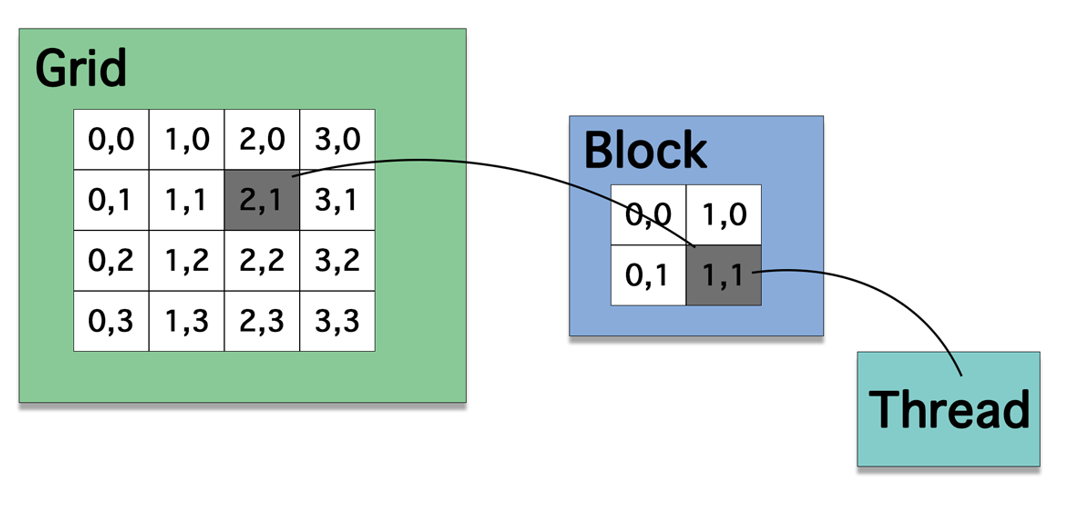
编程模型和硬件的关系
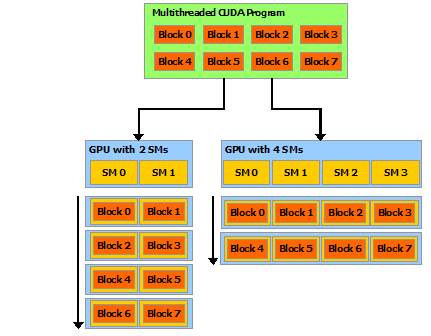
A cooperative thread array (or CTA) is a group of threads that will be co-located on the same multiprocessor(即比如此图中到同一个SM上的所有block的所有thread,它们属于一个CTA)
each block of threads can be scheduled on any of the available multiprocessors within a GPU, in any order(指block之间的顺序?), concurrently or sequentially, so that a compiled CUDA program can execute on any number of multiprocessors, and only the runtime system needs to know the physical multiprocessor count.
概念
在CUDA中:host指代CPU及其内存,而用device指代GPU及其内存
- 三类函数:
函数类型 谁执行 谁调用
global 设备端执行 可以从主机调用也可以从某些特定设备调用
device 设备端执行 设备端调用
host 主机端执行 主机调用- device 函数和global函数因为需要在GPU上运行,因此不能调用常见的一些 C/C++ 函数(因为这些函数没有对应的 GPU 实现)
- 典型的CUDA程序的执行流程如下:
分配host内存,并进行数据初始化;
分配device内存,并从host将数据拷贝到device上;
调用CUDA的核函数在device上完成指定的运算;
将device上的运算结果拷贝到host上;
释放device和host上分配的内存。
编程举例
一维数组加法x+y->z
// __global__ 表示在device上执行,从host中调用
// 两个向量加法kernel,grid和block均为一维
// 每个thread的任务是“跨步”对位加法
__global__ void add(float* x, float * y, float* z, int n){
// 获取全局索引:这个thread的indx,这是第几个thread
int index = threadIdx.x + blockIdx.x * blockDim.x;
// 步长:共有这么多thread
int stride = blockDim.x * gridDim.x;
for (int i = index; i < n; i += stride){
z[i] = x[i] + y[i];
}
}
int main(){
int N = 1 << 20;
int nBytes = N * sizeof(float);
// 申请host内存
float *x, *y, *z;
x = (float*)malloc(nBytes);
y = (float*)malloc(nBytes);
z = (float*)malloc(nBytes);
// 初始化数据
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i){
x[i] = 10.0;
y[i] = 20.0;
}
// 申请device内存
float *d_x, *d_y, *d_z;
cudaMalloc((void**)&d_x, nBytes);
cudaMalloc((void**)&d_y, nBytes);
cudaMalloc((void**)&d_z, nBytes);
// 将host数据拷贝到device
cudaMemcpy((void*)d_x, (void*)x, nBytes, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
cudaMemcpy((void*)d_y, (void*)y, nBytes, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
// 定义kernel的执行配置
dim3 blockSize(256);
dim3 gridSize((N + blockSize.x - 1) / blockSize.x);
// 执行kernel
add << < gridSize, blockSize >> >(d_x, d_y, d_z, N);
// 将device得到的结果拷贝到host
cudaMemcpy((void*)z, (void*)d_z, nBytes, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
// 检查执行结果
float maxError = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
maxError = fmax(maxError, fabs(z[i] - 30.0));
std::cout << "最大误差: " << maxError << std::endl;
// 释放device内存
cudaFree(d_x);
cudaFree(d_y);
cudaFree(d_z);
// 释放host内存
free(x);
free(y);
free(z);
return 0;
}