GraphChi: Large-Scale Graph Computation on Just a PC | USENIX
2012 OSDI
Parallel Sliding Windows (PSW)
关键:以interval为单元的BSP(Bulk-Synchronous Parallel);设计存储layout,使得获取一个interval中所有顶点的邻居只需要 顺序 访问全图磁盘存储 一次
回忆阅读推荐:3.6 Analysis of the I/O Costs
PSW processing a interval
1. load subgraph
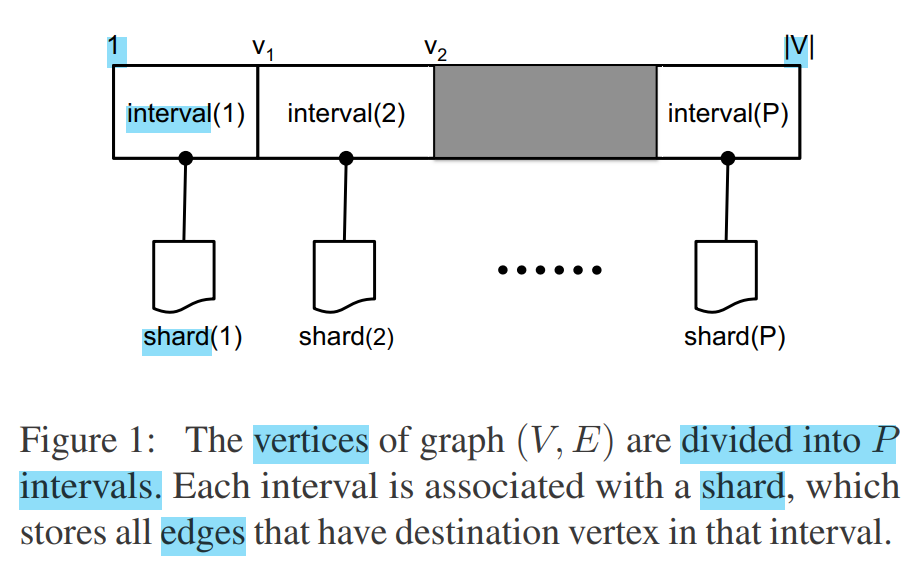
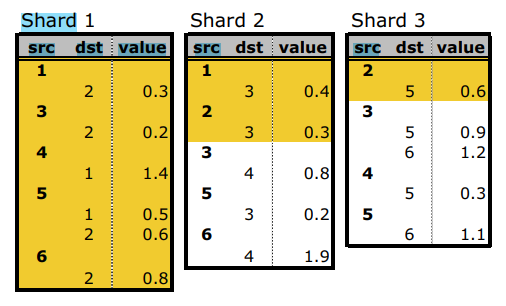
- For each interval, we associate a shard, which stores all the edges that have destination in the interval. Edges are stored in the order of their source(看下图的shard1中的src列,顶点是in order的)
- Intervals are chosen to balance the number of edges in each shard
- 且interval的划分就是对顶点1->|V|这个长区间进行划分(从而在前面的interval中的顶点id小于后面的interval中的顶点id)
- For each interval, we associate a shard, which stores all the edges that have destination in the interval. Edges are stored in the order of their source(看下图的shard1中的src列,顶点是in order的)
- requires only P sequential disk reads to process each interval
【问题】可是就按照邻接表(出邻居)随机存储所有顶点的邻居的话,想要获取一个顶点集合的所有出边和入边,对于磁盘的访问也是可以只要P sequential disk reads的呀?【解答】是的,但是邻接表是对于每个顶点获取一次邻居都需要P sequential disk reads,而这个方法是对于一个interval中所有顶点获取邻居只需要P sequential disk reads
2. Parallel Updates
- executes the user-defined update-function for each vertex( in this interval) in parallel
- vertices that have edges with both end-points in the same interval are flagged as critical, and are updated in sequential order
3. write back
把subgraph中有更新的edge value写回,文章中没有提出新的idea,只是分析了一下写回对于磁盘的访问
例子
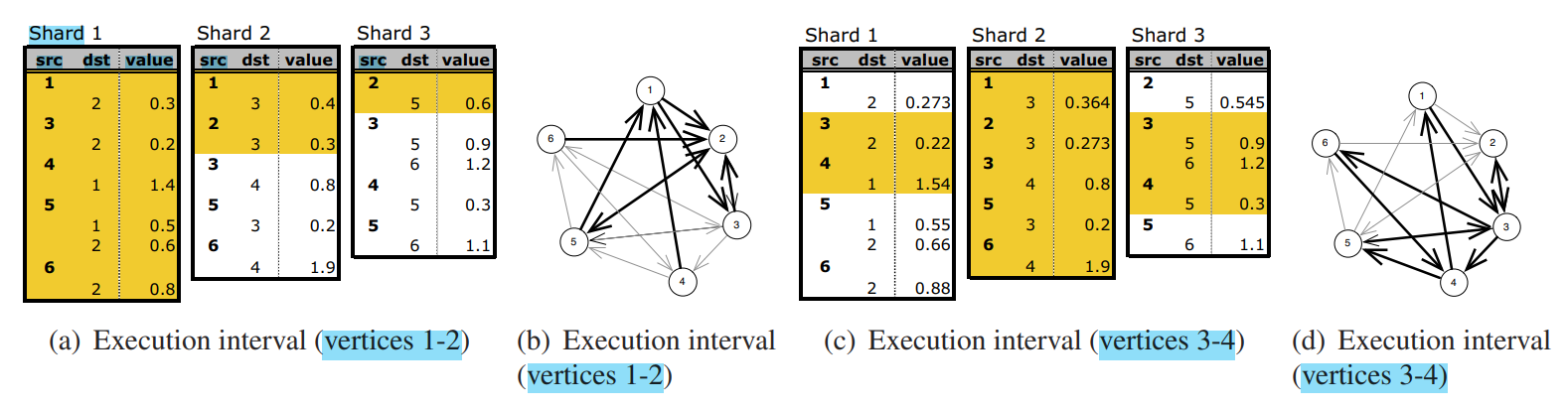
remark
- graph traversals or vertex queries are not efficient in the model, because loading the neighborhood of a single vertex requires scanning a complete memory-shard.



