重定向
举例
#include <iostream>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
/*redirect stdout to file*/
int pfd = open("file", O_WRONLY | O_CREAT, 0777); // now pfd is descriptor to "file"
int saved = dup(1); // now 1 and saved both are descriptor to STDOUT
// int dup2(int oldfd, int newfd);
dup2(pfd, 1); // would close descriptor 1 first, then now 1 and pfd both are descriptor to "file"(pfd previously pointed to)
close(pfd); // close descriptor pfd
cout << "This goes into file" << endl;
// fflush(stdout); // NOTE that endl or fflush(stdout) after printf is necessary to flush content in buffer into file
/*restore stdout*/
dup2(saved, 1); // would close descriptor 1 first, then now 1 and saved both are descriptor to STDOUT(saved previously pointed to)
close(saved); // close descriptor saved
cout << "This goes into console" << endl;
return 0;
}
RAII
异常处理时c++编译器保证会(按顺序)调用所有对象的析构函数,因此把重定向和恢复操作封装到类中会异常安全
上面举例那种,如果在重定向之后、恢复之前程序abort了,则不会进行stdout恢复
全局一个实例
#include <iostream>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
using namespace std;
// implement redirect stdout in class: exception safety
// destructors of all objects are ensured to be called when exception occurs(ensured by compiler)
// redirect stdout to file when constructing instance, restore when destructing
// NOTE: only one success instance is allowed
class RedirectStdout
{
int saved;
int redirected_success;
static int success_instance_count;
public:
int is_success()
{
return redirected_success;
}
// redirect stdout to file
RedirectStdout(const char *file)
{
if (success_instance_count == 1)
{
cout << "only one success instance is allowed!" << endl;
redirected_success = 0;
return;
}
// TODO: check these syscall's return value
// now 1 is descriptor to STDOUT
int pfd = open(file, O_WRONLY | O_CREAT, 0777); // now pfd is descriptor to "bin/.gconsole_tmp_out"
saved = dup(1); // now 1 and saved both are descriptor to STDOUT
// int dup2(int oldfd, int newfd);
dup2(pfd, 1); // would close descriptor 1 first, then now 1 and pfd both are descriptor to "bin/.gconsole_tmp_out"(pfd previously pointed to)
close(pfd); // close descriptor pfd
redirected_success = 1;
++success_instance_count;
}
// fflush and restore stdout
~RedirectStdout()
{
if (redirected_success)
{
--success_instance_count;
// TODO: check these syscall's return value
fflush(stdout); // NOTE that flush the buffer is necessary to indeed push content into file
dup2(saved, 1); // would close descriptor 1 first, then now 1 and saved both are descriptor to STDOUT(saved previously pointed to)
close(saved); // close descriptor saved}
}
}
};
int RedirectStdout::success_instance_count = 0; // init to 0
int main()
{
{
RedirectStdout ins1("1"); // success, stdout is redirected to file"1"
cout << ins1.is_success() << endl; // success, print to file"1"
cout << "This goes into file" << endl; // print to file"1"
RedirectStdout ins2("2"); // fail, fail msg print to file"1"
cout << ins2.is_success() << endl; // print to file"1"
RedirectStdout ins3("3"); // fail, fail msg print to file"1"
cout << ins3.is_success() << endl; // print to file"1"
}
// destruct: restore stdout
cout << "This goes into console" << endl;
return 0;
}
栈式重定向
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <stack>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
using namespace std;
template <typename T>
void print_stk(stack<T> arr)
{
cout << "[sz:" << arr.size() << "] ";
while (arr.empty() == 0)
{
cout << arr.top() << " ";
arr.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}
// if <des> is descriptor to <file>, then we call <des>'s refer is <file>
// construct: redirect descriptor 1's refer ori_file to file(constructor's param)(and push ori_file to static stk top)
// destruct: restore descriptor 1's refer to stk top(and pop stk)
// static stk design ensures when there's no RedirectStdout instance, descriptor 1's refer is stdout
class RedirectStdout
{
public:
static stack<int> ori_file_stk;
/* redirect descriptor 1's refer ori_file to file(and push ori_file to static stk top) */
// append: if set, then open file with |O_APPEND
RedirectStdout(const char *file, int append = 0)
{
// TODO: check these syscall's return value
// now 1 is descriptor to ori_file(if stk is empty, ori_file is STDOUT; else ori_file is stk.top())
int pfd;
if (append)
{
pfd = open(file, O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_APPEND, 0777);
}
else
{
pfd = open(file, O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0777);
}
// now pfd is descriptor to file
int saved = dup(1); // now 1 and saved both are descriptor to ori_file(1 previously refer to)
// int dup2(int oldfd, int newfd);
dup2(pfd, 1); // would close descriptor 1 first, then now 1 and pfd both are descriptor to file(pfd previously refer to)
close(pfd); // close descriptor pfd
ori_file_stk.push(saved);
// now saved(stk.top()) is descriptor to ori_file, 1 is descriptor to file
}
/* fflush and restore descriptor 1's refer to stk top(and pop stk) */
~RedirectStdout()
{
// TODO: check these syscall's return value
fflush(stdout); // NOTE that flush the buffer is necessary to indeed push content into file
int saved = ori_file_stk.top();
ori_file_stk.pop();
dup2(saved, 1); // would close descriptor 1 first, then now 1 and saved both are descriptor to "saved previously refer to"
close(saved); // close descriptor saved
// now only 1 is descriptor to "saved previously refer to"
}
};
stack<int> RedirectStdout::ori_file_stk;
int main()
{
print_stk<int>(RedirectStdout::ori_file_stk); // print in console: {}
// now 1 refer to STDOUT
{
RedirectStdout ins1("ins1");
// now 1 refer to "ins1"
print_stk<int>(RedirectStdout::ori_file_stk); // print in ins1: {des_to_STDOUT}
{
RedirectStdout ins2("ins2");
// now 1 refer to "ins2"
print_stk<int>(RedirectStdout::ori_file_stk); // print in ins2: {des_to_ins1,des_to_STDOUT}
}
// ins2 destruct: now 1 refer to "ins1"
print_stk<int>(RedirectStdout::ori_file_stk); // print in ins1: {des_to_STDOUT}
}
// ins1 destruct: now 1 refer to STDOUT
print_stk<int>(RedirectStdout::ori_file_stk); // print in console: {}
return 0;
}
文件权限编码 chmod
https://digitalfortress.tech/php/difference-file-mode-0777-vs-777/
如何编码
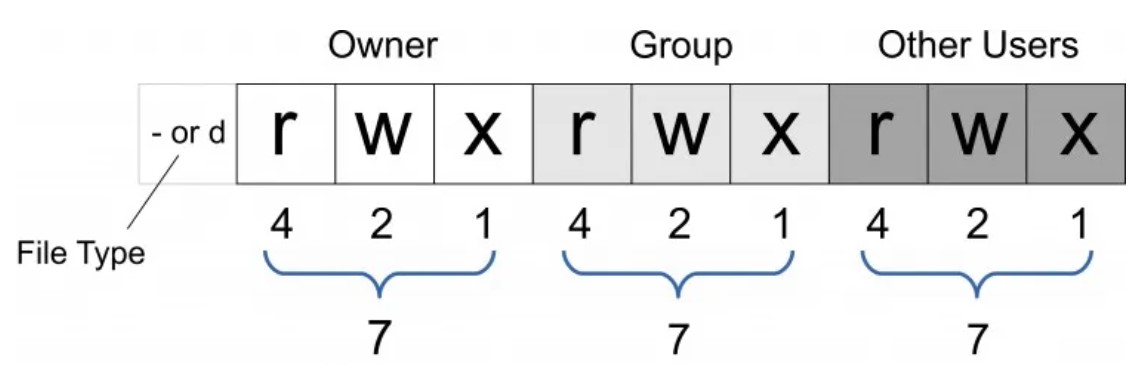
对于posix接口:
- parameter you pass to mkdir() is interpreted as decimal if it isn’t preceded by a 0
- 如果前面有0则是被当作16进制数翻译
因此777 and 0777有区别:
0777 (octal) == binary 0b 111 111 111 == permissions rwxrwxrwx (== decimal 511)
777 (decimal) == binary 0b 1 100 001 001 == permissions sr----x--x (== octal 1411)
对于chmod
- chmod interprets all numeric arguments as octal,则777 and 0777无区别
- 一个计算器:https://chmodcommand.com/
dup dup2
dup, dup2, dup3 - duplicate a file descriptor
#include <unistd.h>
int dup(int oldfd);
int dup2(int oldfd, int newfd);
dup
The dup() system call ++allocates a new file descriptor++ that ++refers to the same open file++ description as the descriptor oldfd.
The new file descriptor number is guaranteed to be the lowest-numbered file descriptor that was unused in the calling process.
After a successful return, the old and new file descriptors may be used interchangeably(毕竟它们指向相同的文件).
Since the two file descriptors refer to the same open file description, they share file offset and file status flags;
(for example, if the file offset is modified by using lseek(2) on one of the file descriptors, the offset is also changed for the other file descriptor.)
The two file descriptors do NOT share file descriptor flags (the close-on-exec flag). The close-on-exec flag (FD_CLOEXEC; see fcntl(2)) for the duplicate descriptor is off.
dup2
++the file descriptor newfd++ is adjusted so that it now ++refers to the same open file description as oldfd.++
If the file descriptor newfd was previously open, it is closed
before being reused; the close is performed silently (i.e., any
errors during the close are not reported by dup2()).
return
On success, these system calls return the new file descriptor.
On error, -1 is returned, and errno is set to indicate the error.



